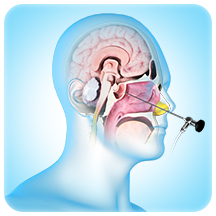
Endoscopic Endonasal Neurosurgery
Endoscopic endonasal approach (EEA) is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows your surgeon to treat tissue damage and tumours near the spine or brain by utilising an endoscope placed through the nose and sinuses.
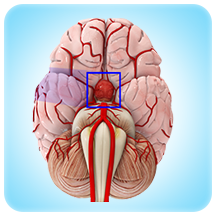
Pituitary (including difficult revisional/ previously operated patients)
Pituitary tumours are abnormal growths within the pituitary gland, a small gland located near the base of the brain. Pituitary tumours can be either functioning or non-functioning. Functioning tumours secrete pituitary hormones that can lead to a clinical syndrome, while non-functioning tumours are those that can cause a syndrome by not secreting pituitary hormones.

Schwannoma
A schwannoma is the abnormal growth of Schwann cells, which line and insulate nerves. It is usually benign and rarely spreads to affect other tissues and organs, but malignant schwannomas that spread are called neurofibrosarcomas or malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours (MPNSTs). The cancer can occur anywhere in the body but the most common areas include:
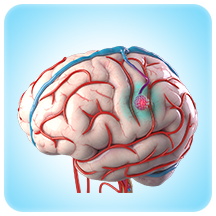
Cavernous Malformations (including deep seated and brainstem)
A cavernous malformation is a rare type of vascular condition characterised by clusters of tiny blood vessels or capillaries in the brain that is irregular and enlarged in structure. These capillaries can vary in size from 2 millimetres to 10 centimetres in diameter and have abnormally thin walls that lack other supportive tissues, like elastic fibres, which typically makes them stretchy. As a result, the capillaries are susceptible to leakage, which can trigger serious health issues related to this condition.

Arteriovenous Malformations
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of the blood vessels that connect the veins and arteries in your brain. An AVM can develop anywhere in the body, but it is more common in the brain and spine.
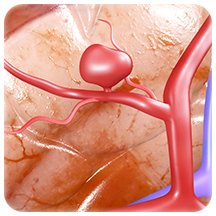
Aneurysms
A brain aneurysm is the ballooning of a weak area on the wall of an artery in the brain. An aneurysm can leak or rupture causing blood to escape into the brain. This is an emergency condition as the blood can damage brain tissue and increase pressure inside the skull, disrupting oxygen supply to the brain, which can lead to unconsciousness or even death. Brain aneurysms usually develop in the arteries at the base of the brain, at weak points where the arteries branch off or fork. They are more common in women than in men. Substance abuse, head injury, arteriosclerosis (hardening of the blood vessels), high blood pressure, ageing, certain congenital diseases, and positive family history increase your risk of developing a brain aneurysm.
Degenerative Spinal Conditions
A degenerative condition is a continuous deterioration of a tissue or an organ in your body over time.

Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Neurosurgery
Minimally invasive endoscopic neurosurgery is a surgical procedure for the treatment of brain tumours and certain spine disorders such as herniated discs and compression fractures. It is performed through tiny incisions with the help of an endoscope, a flexible tube that contains a light source and tiny camera to capture detailed images of the internal tissues and blood vessels. This helps your neurosurgeon perform the surgery with accuracy.

Endoscopic Pituitary/Extended Transphenoidal Tumour Resection
An endoscopic pituitary/extended transsphenoidal tumour resection is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an endoscope, a thin tubular instrument with a camera, light, and a magnifying lens attached at the end, and special instruments are passed through the nose to surgically remove pituitary tumours from the pituitary gland and skull base. Transsphenoidal refers to approaching the treatment area through the sphenoid sinus - a hollow area in the skull behind the nasal passages and beneath the brain. The wall behind the sinus covers the pituitary gland.

Microvascular Surgery
Microvascular surgery or microsurgery is a surgical technique for joining or repairing the damaged blood vessels and nerves during reconstructive surgery of body parts. Reconstructive surgery restores the functioning of the body parts by improving circulation.

Skull Base Surgery
Skull base surgery is usually performed to remove a tumor or an abnormal growth in the base of the skull. It may be performed as an open surgery or by minimally invasive techniques using an endoscope.
Craniopharyngioma
Coming Soon
Skull Base Meningiomas
Coming Soon
Chordoma & Chondrosarcoma
Coming Soon




